It’s a well-known fact that backlinks are one of the foundations of SEO. There are many kinds of strategies for link building, and link farming is one of them. But what are link farms, and what are the consequences of using them?
In this article, we will answer what link farms are and address whether or not they are a link-building strategy worth considering.
By the end, you will learn all you need about link farming and its effects on SEO.
Source: negativeseo.io
What Are Link Farms?
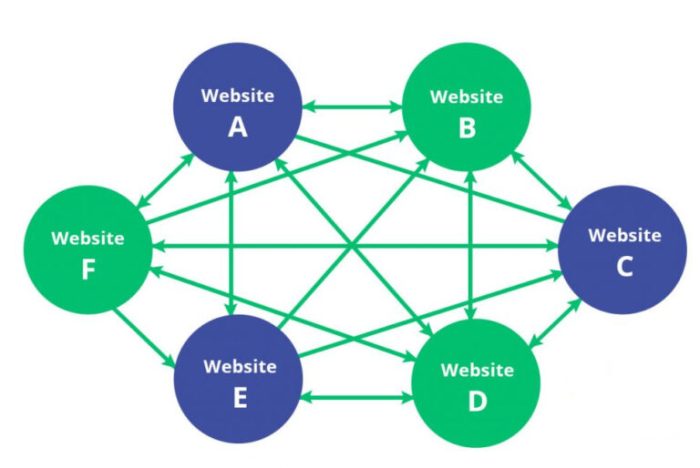
Link farms consist of a series of websites, often owned by the same individual or company, with the sole purpose of linking with each other to boost their rankings in the SERPs.
These websites are not meant to provide valuable information to the readers but instead act as link builders for legitimate sites.
Link farms are similar to Private Blog Networks (PBNs) as they both serve the same purpose.
The only difference is that PBNs aim to provide link juice to sites outside the network.
On the other hand, sites within a link farm are only connected with each other. That said, link farms are identified as black hat link-building entities restricted and penalized by Google.
Link farms of guest posting farms are low-quality websites that churn out irrelevant guest posts, but if you want to avoid those practices and ensure high-quality content, our SEO services for guest posts offer expert assistance in crafting impactful guest posts for reputable platforms.
Let’s examine why link farms are considered a bad practice.
Google’s Battle Against Link Farms
The early 2000s
To understand why link farms are a bad practice, we must explain how Google and other search engines previously viewed this strategy.
During the early years of the new millennium, search engines, specifically Google, hadn’t developed the advanced semantic algorithms they have today.
This means that the algorithms in the past openly supported link farming practices.
In other words, Google ranked websites based on the number of links, not their quality. This gave an advantage to websites with high-volume, low-quality links to rank high in the SERPs.
The introduction of Google Panda and Penguin algorithms
In 2011, Google decided to introduce the Panda algorithm. This was Google’s first serious attempt to battle black hat link-building practices.
The Panda algorithm proved successful as it lowered the ranking of websites with low-quality content. At the same time, it analyzed and promoted sites with fewer links but high-quality content.
Then in 2012, with the introduction of the Penguin algorithm, Google started diminishing the number of black hat link-building practices more extensively.
The Penguin algorithm exclusively targeted manipulative link-building techniques, which directly targeted link farms.
Tips to Identify Link Farms
Before you struggle to obtain a link from any website, you must evaluate several criteria and ensure the website is not part of a link farm.
Here are some things to consider when identifying a potential link farm website:
The design, layout, and content quality
The first and obvious thing you do when you visit any website is to look at its design and layout.
While quality websites have amazing designs and intuitive layouts, sites that are part of a link farm will often have:
- Poor design
- Simple and non-intuitive layout
- Little to no customization
- Low-quality and outdated content
- Content topics from different niches
Here is an example of a link-farming website:
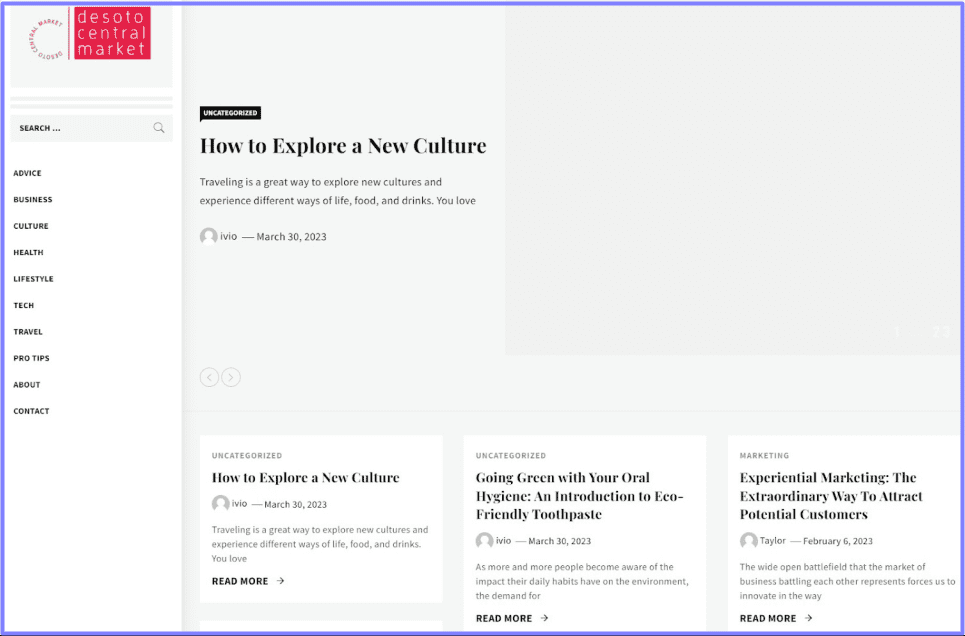
You can see that something is wrong with the design, layout, and, most of all, the content topics of these websites.
The “author” and “about” information
Websites part of a link farm will not display a genuine “author” or “about” section.
Instead, they will have either no author information below the posts or minimal information combined with a fake profile picture.
The “about” page is often filled with short and unclear information, not involving any kind of contact information.
This makes it impossible to determine the person or company behind the site, so it is most likely part of a link-building scheme.
The context of the anchor texts
Anchor texts can be another obvious sign of a link farm website. They are the clickable hyperlinks within the content.
It’s a good practice for the anchor texts to be keyword-rich, but overdoing it is a signal of bad practice. If there are a lot of keyword-rich anchors, then the website is probably part of a black hat link-building scheme.
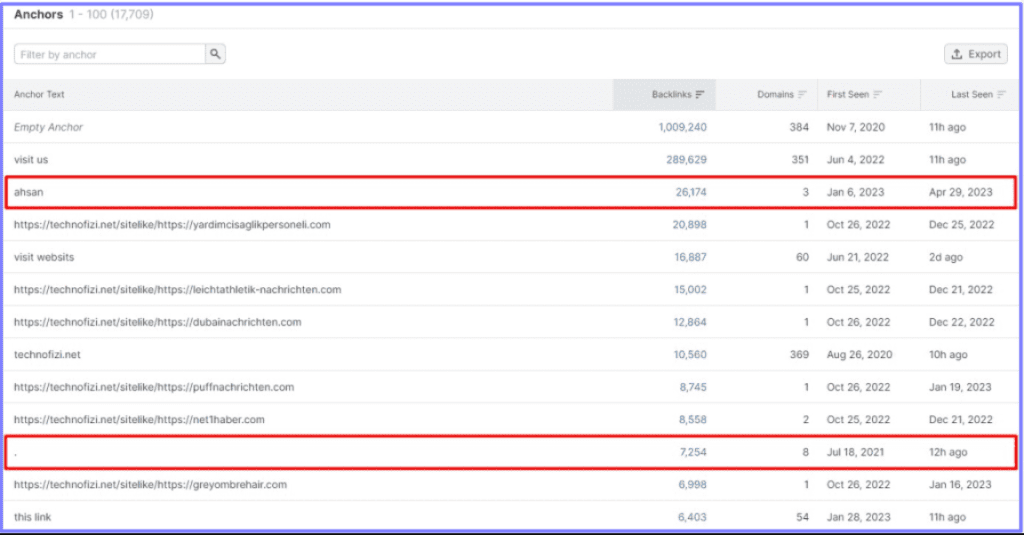
Here’s an example of unnaturally used anchor texts with thousands of backlinks. It’s clear that the intent here is to manipulate links and link juice flow between sites in a link farm.
The number of external links
The number of external links from a website can also indicate that the website is part of a link farm.
External links are essential for SEO, but it’s not a good signal if the webpage links to many sites.
Here’s an example of a suspicious site that might be part of a link farm:
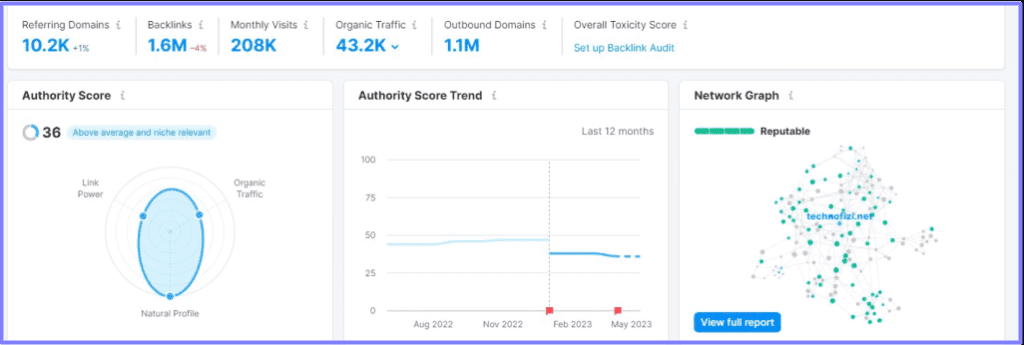
Here, the number of outbound domains is around 1.1 million. This is suspicious and unnatural since the site has only 10.2K referring domains and 1.6 million backlinks. These signals clearly point out a link farm.
On the other hand, here’s what a healthy and authoritative site’s backlink profile looks like:
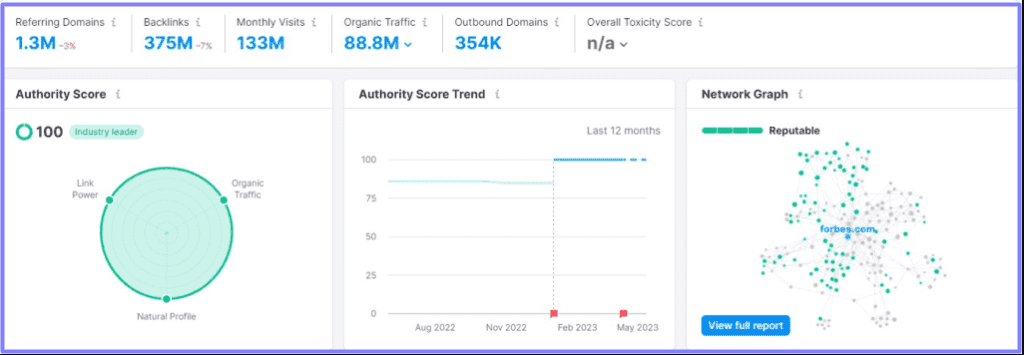
The Risks of Link Farming
We’ve already discussed how Google fights and discredits link farms. So even if you may hear any of the SEO experts claiming that link farms provide a sustainable SEO boost, this is not true.
In any case, what are link farms if not a black hat link-building technique that brings multiple risks? Find out below.
They may only provide short-term results
Even though link farms were able to provide long-term results in the past, that is not the case today.
With the constant improvement of search engine algorithms, link farms are often caught and penalized as quickly as they become operational. Even if the owner of a link farm tries to avoid search engine penalties, there is no guarantee that that might not happen at any time.
They offer low-link quality
Not all backlinks are created equal. Each backlink can provide different effects, depending on multiple factors.
While high-quality backlinks can help boost your site’s SEO rankings, low-quality backlinks can expose your site to a constant penalty threat from Google or other search engines.
High-quality backlinks are reputable, organic, naturally integrated into content, and come from credible domains.
Backlinks from link farms have all the opposite characteristics.
You risk being penalized by Google
The biggest downside of using low-quality backlinks is the risk of being penalized by search engines like Google.
This also applies to low-quality backlinks used within the content.
A clear indicator of this may be a sudden drop in traffic to your website. This happens because your site has been pushed further down the SERPs or completely removed from them. You will not be notified if this happens.
In this case, the best action is to rectify the mistakes, remove links from unwanted websites, and hope your website starts receiving traffic once Google re-evaluates it.
You Might Be Interested: Do Niche Edits Links Work?
Alternatives to Link Farming
So, how can you avoid fake and short-lasting traffic from link farms? Here are a few tips:
Try to acquire organic backlinks
Organic backlinks are the strongest and most long-lasting links that your website can acquire. They are placed on another website naturally, mainly due to the quality of your website’s content.
So the primary factor in acquiring organic backlinks is to provide unique and valuable content that offers readers something they can’t find anywhere else.
This is also the slowest way to build an organic backlink network, but it’s also the most effective in the long run.
Aim for web directories
Web directories are often websites with many links, similar to link farms.
But unlike link farms, directories contain specific and curated content to help those seeking particular information. Link farms are the opposite of directories, as they contain random content that has no informative value.
Directories are also niche-oriented, so they don’t cover broad, random topics like link farms.
All this means that acquiring a backlink from a web directory is an excellent SEO practice.
These sites are often authoritative and well-known in the online community for being reliable sources of information.
Perform regular backlink audits
No matter how careful you are with link building, it can many times happen that your site becomes associated with bad backlinks.
These backlinks may hurt your site’s SERPs rankings without you knowing it.
Performing regular backlink audits is a way to minimize and eliminate this problem.
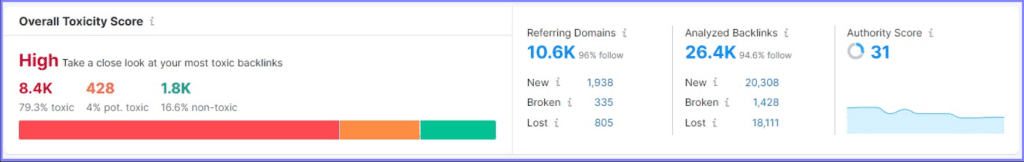
You can use tools like Semrush or Ahrefs to perform a backlink audit. Here’s an example of a domain backlink audit made with Semrush:
As you can see from the example, this website has over 8.4K toxic referring domains, which is one of the reasons its authority score keeps dropping over time.
Conclusion
Link-building remains one of the pillars of SEO.
But link-building strategies have changed significantly over time due to the constant evolution of search engine algorithms.
Link farms may have been effective in the past, but today they are considered an unworthy investment. People who implement them in their marketing strategies will, eventually, experience their negative effects.
Now that you know what are link farms for and how they impact SEO, will you dare to use them to improve your site’s rankings?
Let us know in the comments below.
